Cameras in Medicine
Exceptional precision and performance
Modern technologies have significantly transformed healthcare, particularly through the use of industrial digital cameras. These devices enable physicians to capture detailed visual information, greatly enhancing diagnostic procedures, treatments, and patient monitoring.
Advantages of machine vision cameras in medicine
In our white paper, we explain:
What role machine vision cameras play in medical applications
Which criteria are important when choosing the right camera in medicine
Why color fidelity is crucial in this field
How industrial cameras revolutionized healthcare
Before imaging cameras were available in medical technology, it was often difficult to obtain accurate diagnostic information. For example, procedures known as "exploratory surgery" were widespread in the 1800s, requiring doctors to use invasive surgery methods to make diagnoses. Today, advancements in imaging and vision technologies have resulted in a wide range of camera-based diagnostic devices to simplify these processes.
Typical areas of application:
Fundus cameras for retinal examination in ophthalmology.
Automated microscopy for analysis of body fluids such as blood or urine.
Endoscopes for examination of organs and body cavities.
Intraoral scanners for digital recording of the oral cavity in dentistry.
Digital dermatoscopes for identification and tracking of suspicious skin areas in dermatology.
All of these devices provide information that can contribute to both diagnosis and further treatment in the fields of Medical and Life Sciences.
Advantages of medical cameras at a glance
There are four major advantages that cameras have in the medical field.

Documentation
Digital images allow doctors to examine areas of interest more easily than traditional optical methods. Additionally, these images can be annotated to track suspicious areas over time. All image data can be stored in digital patient records, making it accessible to healthcare professionals globally.
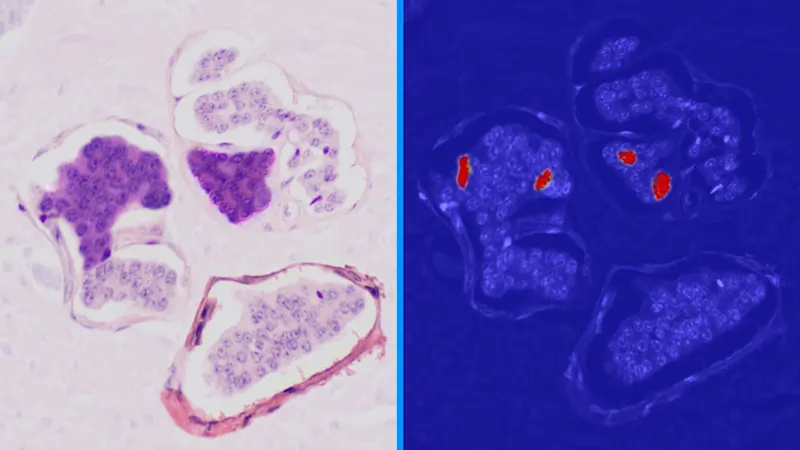
Image analysis
In today's tumor diagnostics, the removal and analysis of tissue sections under the microscope is still a common practice. Automated microscopes can be used to scan the image of the object slide. Modern image analysis algorithms, such as neural networks, can then search the image for suspicious regions which can be presented to pathologists for further analysis. This process occurs within a few minutes, while the manual examination takes several hours and depends on a single individual.

Automation
Two trends are driving development in this area. The increasing demand for multiple diagnostics, influenced by demographic factors, has grown significantly. At the same time, rising labor costs are creating a need for greater automation. For example, barcode-reading classification systems automate the storage of blood sample tubes, reducing the need for manual handling.
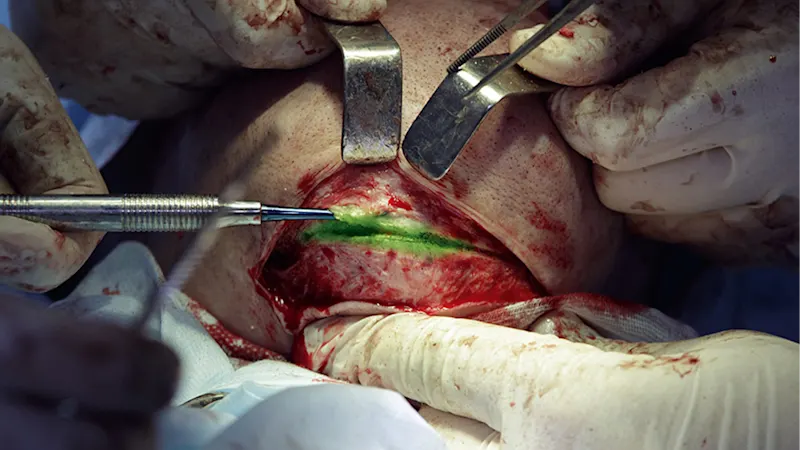
Visualization
In medicine, cameras serve as vital tools in a variety of demanding imaging procedures. For example, endoscopes, equipped with millimeter-sized cameras record the path of the device through the inside of the body. In fluorescence-guided surgery, surgeons can distinguish between healthy and cancerous tissue in real time during the procedure. Fluorescence angiography provides ophthalmologists with information about the condition of the blood vessels in the eye, while hyperspectral cameras differentiate between tissue with good and poor blood supply.
Performance requirements for accurate diagnostics
The diagnostic process often depends directly on the camera image. For this reason, cameras designed for use in medicine must meet high performance requirements:
Reliability and robustness: Industrial cameras must be precisely manufactured, durable, and extremely reliable to consistently deliver comparable images. They must be manufactured according to ISO standards to meet the requirements of medical device manufacturers.
High color fidelity: Diagnoses are often based on color information, so the camera must accurately transfer colors to the digital image. The color visible on the monitor must match real world conditions.
Long-term availability: Since the certification of diagnostic devices is time-consuming, cameras must ensure long term availability.
Correct range of functions: In addition to raw data, cameras must offer advanced features such as color interpolation, color calibration, sharpness correction, and more to meet the requirements.
Areas of application of medical cameras at a glance
Digital image processing opens up a wide range of possibilities for research, analysis, and diagnosis of diseases.
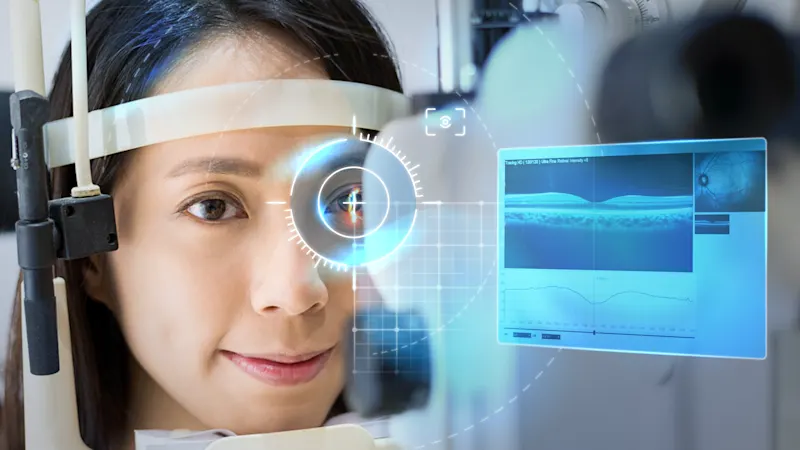

Ophthalmology
Imaging technologies play an important role in ophthalmology. Medical cameras, such as modern OCT or fundus cameras for retinal examination, simplify and improve the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases as well as the mobility of treatment methods. Factors such as precise color reproduction, reproducibility, sensitivity, and excellent image quality with optimal speed and resolution are decisive. Basler offers high-performance technologies for a wide variety of applications.
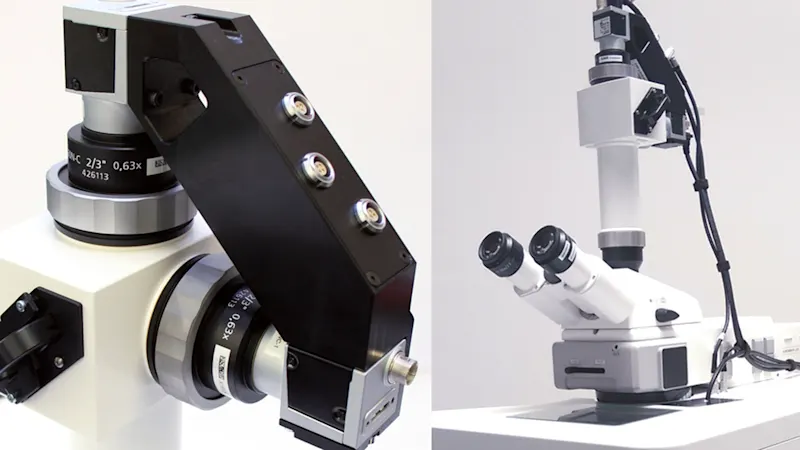

Laboratory equipment and automation
Whether it's process automation, quality control, or bio-imaging, state-of-the-art industrial cameras have become an essential component of medical diagnostic laboratory equipment. They deliver high speed, resolution, reliability, and superior image quality for consistent analyses and efficient sample throughput. Our cameras offer these qualities and can be seamlessly integrated into your automated laboratory equipment.
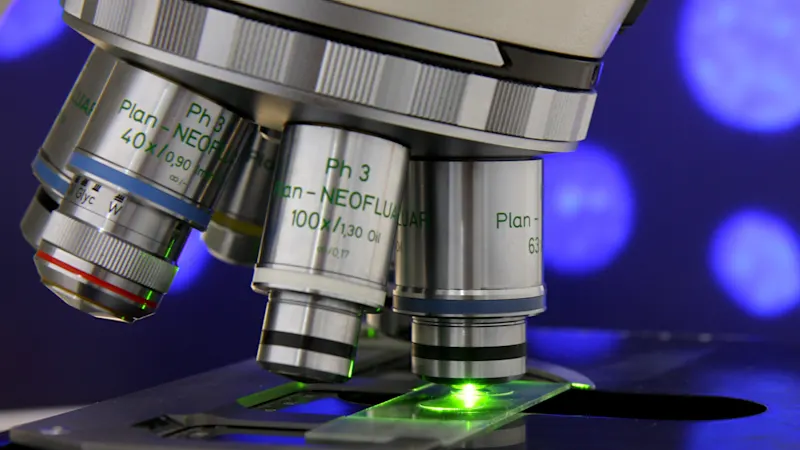

Microscopy
From medical and biological research to materials science, pharmaceutical testing, and diagnostics, camera technologies play a central role in image acquisition and processing in optical microscopy. Our cameras provide exceptional image quality in real time, excellent color reproduction, and a wide dynamic range. They enable precise, reproducible analysis of even the smallest structures and are suitable for both conventional light microscopy and fluorescence microscopy.
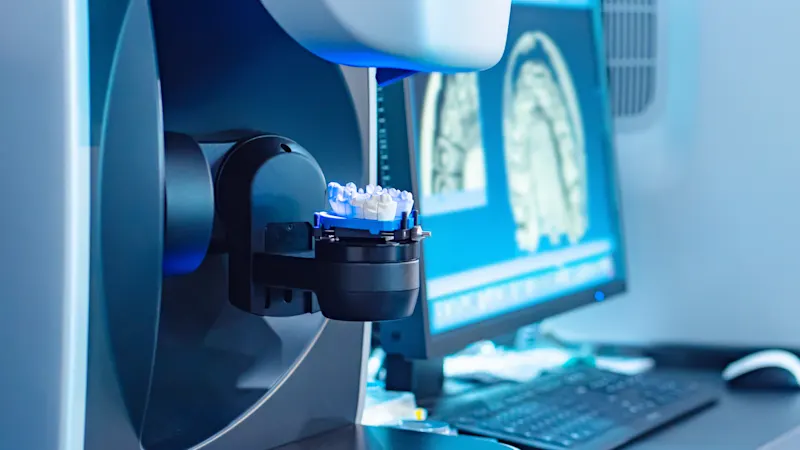
Dentistry
Dentistry relies on the latest technologies powered by high-performance cameras with fast speed, optimal resolution, and sensitivity. With their compact design, our cameras provide the ideal conditions for seamless integration into these advanced technologies.
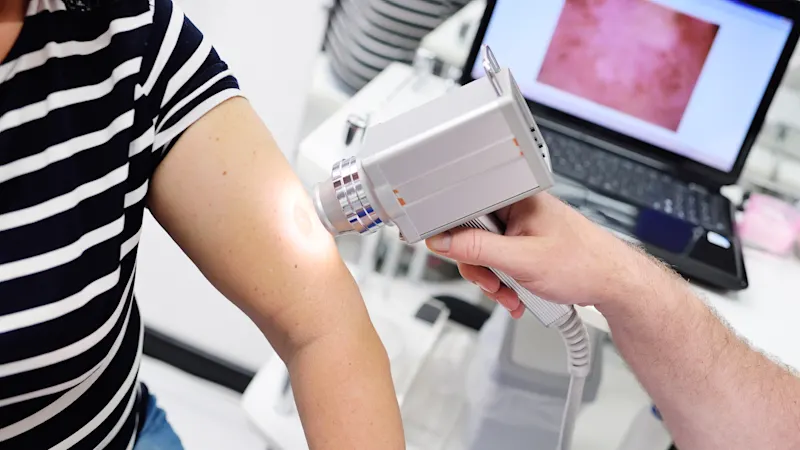
Dermatology
During a dermatoscopic examination, suspicious skin changes are photographed. For an accurate assessment by the dermatologist, software provides a computer-aided analysis of the images. An important prerequisite for the evaluation of the acquired images is standardized image acquisition. Our cameras ensure this by compensating for different shooting conditions such as light and angle. This means that the images are comparable over a longer period of time. In addition, our cameras ensure color fidelity so that patients receive the most reliable diagnosis possible.
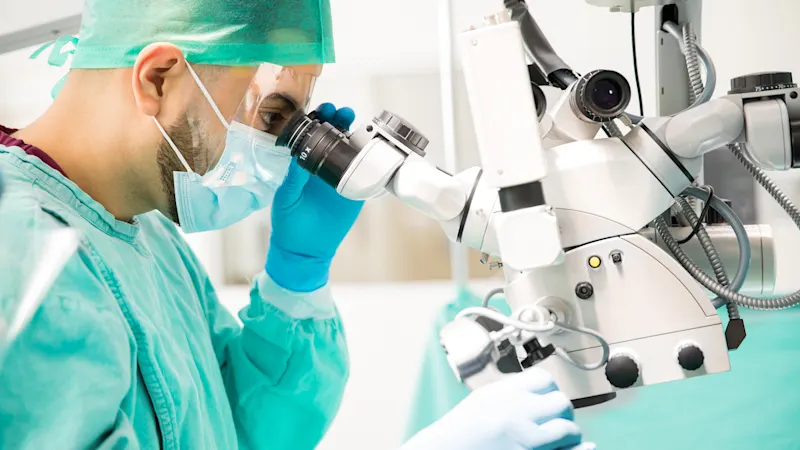

Operating theatres
Cameras in the operating theater are integrated into compact devices mounted on swivel arms above the operating table, as well as in endoscopes for minimally invasive surgeries. These cameras allow a patient's procedure to be viewed from multiple angles and broadcast live. Additionally, recorded footage can be utilized for training and consultation purposes. Our cameras are known for their high resolution and exceptionally low failure rate.
Cameras in medicine
Focus on data protection and security
Medical image and video recordings often include sensitive patient data. To preserve patient trust, protection, and privacy, strict security measures are essential when using medical cameras. Key measures include authorized access restrictions, encrypted data transmission, and password protection. Regular maintenance of the cameras is also crucial to ensure they function properly and do not present safety risks. Additionally, patients must be informed about the use and storage of their data and provide their consent beforehand.
The future of medical image processing
With lower costs and smaller dimensions, more medical devices will be equipped with machine vision in the future, making these advanced devices increasingly common in medical facilities. Industrial cameras are ideal for use in the medical field, offering a combination of advanced sensor technology, high resolution, and exceptional image quality.
Our products for image processing in medicine
Benefit from the specially designed Basler MED ace camera series along with our experience in developing individual machine vision solutions for your requirements.
